Cutting Alumina Ceramic: What Should You Pay Attention to?
What Is Alumina Ceramic Substrate?
Alumina ceramic substrate is a type of ceramic base material made mainly from aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). It is widely used in electronics, power modules, LED lighting, and aerospace applications due to its excellent insulation, durability, and heat resistance. Manufacturers choose alumina because it combines mechanical strength and thermal stability in one material.
Substrates made from alumina ceramics are flat, hard plates that support electronic circuits and components. They can withstand high temperatures and chemical exposure without degrading, which makes them reliable in harsh environments.

Types of Alumina Ceramic
Alumina ceramic comes in several grades, usually defined by purity levels and application needs. Common types include:
1. 96% Alumina (Al₂O₃):
This is the standard type used for general electronics. It offers good mechanical and electrical performance.
2. 99% Alumina:
Used in high-performance applications where better thermal conductivity and higher dielectric strength are needed.
3. 99.5% and above:
These ultra-high purity types are often used in semiconductor packaging or precision medical devices.
You must to know: the higher the purity, the more refined the performance. But this also affects how the material behaves during cutting.
Alumina Ceramic Substrate Properties
Before cutting alumina, it’s important to understand its key properties:
- Hardness: Alumina is extremely hard — second only to diamond on the Mohs scale.
- Brittleness: Though tough, alumina is still brittle. It can crack if handled improperly.
- Thermal Conductivity: It dissipates heat well, especially at higher purity levels.
- Electrical Insulation: Excellent dielectric properties make it ideal for circuits.
- Chemical Resistance: It resists corrosion and chemical reactions in aggressive environments.
- These properties make alumina reliable — but also tricky to machine.
Why Need to Cut an Alumina Ceramic?
Cutting alumina is often required for custom sizes, slotting, trimming edge irregularities, or creating mounting holes. It also helps:
- Fit the substrate into a device or housing
- Make electrical isolation paths
- Shape the substrate for heat dissipation
- Integrate with other materials like metals or adhesives
Standard substrates are typically square or rectangular. But real-world applications often need specific shapes or dimensions. That’s where precision cutting becomes essential.

Methods of Cutting Alumina Substrate
Cutting alumina isn't like cutting plastic or metal. Its hardness and brittleness demand specialized tools and techniques. Here are the most common methods used:
1. Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is popular for thin alumina (under 1mm). It uses high-energy beams to vaporize material with minimal contact. Benefits include clean edges, low risk of chipping, and precise control.
Limitations:
It may not be suitable for thick ceramic. Also, it generates heat, which could create microcracks if not well-controlled.
2. Dicing Saw
A dicing saw uses a diamond blade to cut the ceramic with high precision. It's widely used for making multiple small substrates from a large panel.
Pros:
- Accurate
- Repeatable
- Scalable for mass production
Cons:
- May leave stress on edges
- Requires coolant to avoid overheating
3. Mechanical Scribing and Breaking
This is an old-school but cost-effective method. It involves scoring the ceramic and snapping it along the line.
Good for:
- Low-volume production or prototypes.
Risk:
- Cracks can propagate unpredictably.
4. Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water mixed with abrasive particles to cut through alumina.
Advantages:
- No heat zones
- Less stress compared to laser
Downsides:
- Lower precision and potential contamination.
5. CNC Machining
For complex shapes or multi-step fabrication, CNC routers with diamond-coated tools can be used. It’s ideal for drilling, slotting, and shaping.
Drawback:
- Slower and more expensive for thin substrates.
Which Alumina Ceramic Shape Is Best?
There’s no single "best" shape for alumina ceramics. The ideal form depends on your application:
- Rectangular: Best for multilayer circuits, LEDs, and general electronics.
- Circular: Common in sensor bases or high-frequency RF designs.
- Custom Shapes: For modules, hybrid circuits, or special mechanical fixtures.
When choosing a shape, consider:
- Heat flow and dissipation
- Mounting or soldering points
- Electrical isolation needs
- Space constraints in your assembly
It’s also wise to design with manufacturability in mind. Simple shapes are easier and cheaper to cut.
What Should You Pay Attention to When Cutting Alumina?
Cutting alumina is a sensitive process. Even a small error can crack the substrate or damage your tools. Here’s what to focus on:
1. Tool Selection
Always use diamond-tipped tools or lasers designed for ceramics. Standard tools will wear out fast and damage the material.
2. Cutting Speed and Feed Rate
Too fast, and the ceramic may crack. Too slow, and your tool might overheat. Find a balanced speed based on thickness and tool type.
3. Support and Clamping
Improper support causes vibration, leading to edge chipping or microfractures. Use soft pads and uniform pressure during machining.
4. Coolant Use
Always use coolant when sawing or drilling. It reduces heat and prevents stress buildup.
5. Cleanliness
Dust and debris from cutting alumina are abrasive. Clean the work area and parts to avoid contamination in downstream processes.
6. Edge Finish
Check for microcracks, burrs, or residue. These flaws can cause failure during thermal cycling or assembly.
7. Post-Cutting Inspection
Use microscopes or cameras to inspect the surface and edges after cutting. Optical inspection helps spot invisible damage.
If you're unsure, partner with a professional ceramic cutting service — especially for high-precision or high-volume jobs.
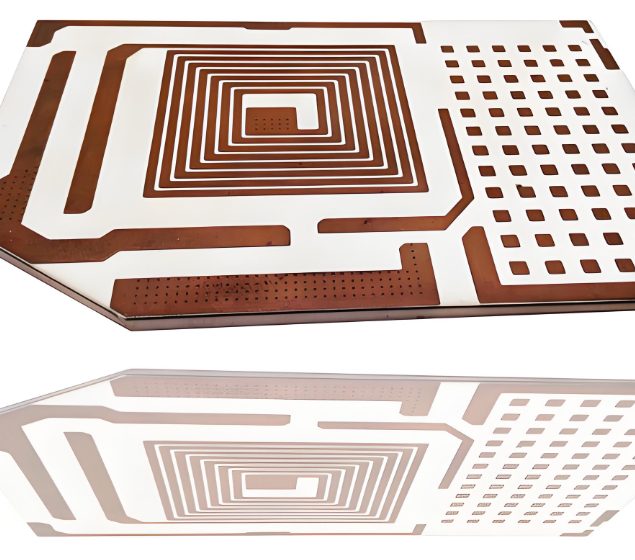
Reliable Alumina Ceramic Substrate Supplier – BstCeramic PCB
At BstCeramic, we specialize in manufacturing and cutting alumina ceramic substrates with high precision and consistent quality. Our engineering team understands the challenges of working with brittle ceramic materials and uses advanced techniques to reduce risks during fabrication.
We offer:
- 96% and 99% alumina substrates
- CNC machining and laser cutting services
- Custom shapes and hole drilling
- Surface finishing and metallization
- Fast turnaround and strict QC process
Our facility is ISO-certified, and we serve customers in automotive, aerospace, LED, and telecommunication industries. Whether you need small batches or full-scale production, we’re ready to support your project.
Final Thoughts
Cutting alumina isn’t something to take lightly. Its hardness and brittleness require proper tools, techniques, and attention to detail. From choosing the right substrate type to selecting the best cutting method, every step affects your final product quality. If done correctly, alumina substrates offer long-lasting performance in harsh conditions.
Let BstCeramic help you avoid costly mistakes and get precision-cut ceramic parts every time. Reach out to our team at sales@bstceramicpcb.com to discuss your custom requirements today.
FAQs
1. Can I cut alumina ceramic at home?
It’s not recommended. Alumina is extremely hard and brittle, requiring industrial tools and safety precautions.
2. What’s the best method for cutting thin alumina substrates?
Laser cutting is efficient for thin sheets (under 1mm) and offers clean results with low mechanical stress.
3. How do I avoid cracks when cutting alumina?
Use proper support, cooling, and diamond tools. Avoid high speeds and sharp feed rates.
4. Is CNC better than laser cutting for alumina?
CNC is better for complex shapes and thicker pieces. Laser is faster for thin and simple cuts.
5. Can BstCeramic customize alumina substrate shapes?
Yes. We provide custom cutting, hole drilling, and shape design based on your specs.











































 HOME
HOME