What is Aluminum Nitride Ceramic Substrate?
What is aluminum nitride AlN substrate?
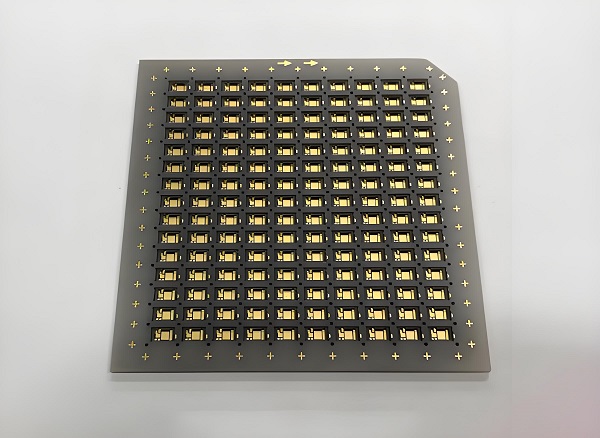
Aluminum nitride (AlN) ceramic substrate is a technical ceramic layer made almost entirely of aluminum nitride. In simple terms, aluminum nitride (AlN) is a crystalline compound of aluminum and nitrogen, and an AlN substrate means a plate or PCB base layer composed of this material. AlN substrates are valued in high-performance electronics for their excellent thermal conductivity and electrical insulation. In practice, AlN ceramic boards carry and cool semiconductor chips, LEDs, power modules and other devices that generate a lot of heat. Put simply, an AlN substrate is a high‐performance ceramic base (sometimes metallized with copper) used wherever heat must be spread and electrical signals must be insulated in demanding industrial or electronic applications.
Aluminum nitride formula
The chemical formula of aluminum nitride is simply AlN – one atom of aluminum (Al) bonded to one atom of nitrogen (N). In IUPAC terms, its molecular formula is AlN with a molecular weight around 40.99. The ratio of aluminum to nitrogen in the compound is 1:1, and this stoichiometry is fundamental in determining the physical and chemical properties of aluminum nitride. In industry, when engineers ask “what is aluminum nitride (AlN),” the answer is that it’s a covalently-bonded ceramic composed of aluminum and nitrogen in equal measure (AlN) with a highly ordered crystal lattice and useful heat‐dissipation properties.
What is aluminum nitride ceramic substrate made of?
An aluminum nitride ceramic substrate is made of high-purity aluminum nitride powder that has been formed and sintered into a solid substrate.
The manufacturing process starts with the selection of high - quality raw materials. The aluminum nitride powder is then mixed with binders and additives to form a homogeneous mixture. This mixture is then shaped into the desired substrate form through processes such as tape casting, pressing, or injection molding. After shaping, the substrate undergoes a high - temperature sintering process.

During sintering, the binders are removed, and the aluminum nitride particles are bonded together to form a dense and strong ceramic structure. Some manufacturers may also add small amounts of other elements or compounds to modify the properties of the substrate, such as improving its mechanical strength or thermal conductivity.
Aluminum nitride material properties
|
Properties |
Value |
|
Color |
Grey |
|
Density |
3.26 g/cm³ |
|
Hardness |
7-8 (Mohs hardness) |
|
Thermal conductivity |
140–180 W/m·K (>300 W/m·K for single-crystal or highly pure AlN) |
|
Dielectric constant |
8.6-9.5 |
|
Resistivity |
~10^10 Ω·cm |
|
Thermal Expansion |
~4.5–5.6×10^−6/K |
|
Mechanical Strength |
~300–350 MPa |
|
Elastic modulus |
300 GPa |
Aluminum nitride thermal conductivity
One of the most important properties of AlN is its high thermal conductivity. At room temperature, the thermal conductivity of AlN can reach up to 170 - 285 W/(m·K), which is much higher than that of many other ceramic materials and even some metals.
In electronic applications, this property is extremely valuable as it enables the rapid dissipation of heat generated by electronic components. For example, in high - power LEDs and power electronics, the use of aluminum nitride substrates can prevent overheating and improve the performance and lifespan of the devices.
What happens when aluminum nitride reacts with water?
When aluminum nitride reacts with water, it undergoes a hydrolysis reaction. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
AlN + 3H₂O → Al(OH)₃ + NH₃
In this reaction, aluminum nitride reacts with water to form aluminum hydroxide and ammonia gas. The reaction is relatively slow at room temperature but can be accelerated by increasing the temperature or in the presence of catalysts.
This reaction needs to be considered in applications where the aluminum nitride substrate may come into contact with water or moisture. For example, in outdoor or humid environments, proper protection measures should be taken to prevent the hydrolysis of the substrate, as the formation of aluminum hydroxide can affect the performance and integrity of the substrate.
How to cut aluminum nitride sheet?
Cutting aluminum nitride sheets requires special techniques due to its hardness and brittleness. Here are some common methods:
- Diamond saw cutting
This is one of the most widely used methods. A diamond - tipped saw blade is used to cut through the aluminum nitride sheet. The diamond particles on the saw blade are hard enough to cut the ceramic material. However, this method can generate a significant amount of heat, so proper cooling is required to prevent damage to the sheet.
- Laser cutting
Laser cutting is a precise method that uses a high - energy laser beam to melt and vaporize the aluminum nitride material. It can achieve very fine cuts with high accuracy. But it also has some limitations, such as the high cost of equipment and the potential for thermal damage to the surrounding area of the cut.

What is aluminum nitrate ceramic PCB used for?
Aluminum nitride ceramic PCBs have a wide range of applications due to their excellent properties:
- High - power electronics
In power amplifiers, converters, and inverters, the high thermal conductivity of aluminum nitride substrates helps to dissipate the large amount of heat generated by high - power components.
- Optoelectronics
For high - power LEDs, aluminum nitride substrates can effectively transfer the heat away from the LED chips, which improves the luminous efficiency and extends the lifespan of the LEDs. In laser diodes, the substrate's high thermal conductivity and electrical insulation properties are also crucial for maintaining the performance of the diodes.
- Aerospace and defense
In aerospace and defense applications, where reliability and performance under harsh conditions are essential, aluminum nitride ceramic PCBs are used in radar systems, communication equipment, and avionics. If your products will be used in aerospace applications, a AS9100D certified manufacturer is must, which can ensure the highest quality and make sure all the processes are under strictly control that conform to quality control system.
How expensive is aluminum nitride ceramic substrate?
The cost of aluminum nitride ceramic substrates is relatively high compared to some other types of substrates, such as FR4. Several factors contribute to the high cost:
- Raw material cost
The production of high - purity aluminum nitride powder is a complex and costly process. The raw materials and the purification techniques required to obtain high - quality powder add to the overall cost.
- Manufacturing complexity
The manufacturing process of aluminum nitride substrates involves high - temperature sintering and precise shaping techniques. These processes require specialized equipment and skilled labor, which increase the production cost.
- Low production volume
Compared to more common substrates, the production volume of aluminum nitride substrates is relatively low. This lack of economies of scale also contributes to the higher cost per unit.
What is the difference between ceramic substrate and FR4?
FR4 is a popular PCB material made from fiberglass and epoxy resin. It’s inexpensive, easy to work with, and used in many consumer electronics. However, it doesn’t compare well to aluminum nitride in high-performance settings.
|
Feature |
Aluminum Nitride |
FR4 |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
170–200 W/m·K |
~0.3 W/m·K |
|
Electrical Insulation |
Excellent |
Good |
|
Thermal Expansion |
Close to silicon |
Larger mismatch |
|
Durability |
Brittle but strong |
Flexible |
|
Cost |
Higher |
Lower |
If your application runs cool and doesn’t need top-tier performance, FR4 is fine. But when heat and voltage matter, aluminum nitride ceramic PCB is a much better option.
Why Choose Best Technology for Aluminum Nitride Substrates?
When it comes to ceramic PCBs, Best Technology stands out for quality, customization, and technical support. We specialize in aluminum nitride ceramic substrates that meet the needs of industries where performance is everything. Here’s what makes us popular:
- Global Certifications: Our production meets ISO9001, ISO13485 (medical), IATF16949 (automotive), and AS9100D (aerospace) standards.
- Advanced Equipment: From laser cutting to sintering, we use precise tools that deliver consistent results.
- Full MES Traceability: Every step of production is monitored and recorded for full quality control.
- Skilled Engineering Team: We work closely with clients to fine-tune every design, from thermal layout to electrical optimization.
- Fast Turnaround: We deliver samples and production runs on time—without compromising quality.
Whether you're working on a ceramic PCB prototype or scaling to mass production, we’re here to support your success.
FAQs
1. Is aluminum nitride toxic?
No. In solid form, AlN is not toxic. However, inhaling its dust can irritate the respiratory system, so safety precautions are necessary when handling powder.
2. Can aluminum nitride be used in flexible electronics?
No. AlN is a rigid ceramic and doesn’t bend. It’s suited for solid, flat PCB designs.
3. Does aluminum nitride perform better than alumina?
Yes. AlN has much higher thermal conductivity, making it better for heat-intensive circuits.
4. What thicknesses are available for aluminum nitride sheets?
Most common sizes range from 0.25mm to 1.0mm, but custom thicknesses can be made to order.
5. Can aluminum nitride be used outdoors?
Yes, but it needs a protective coating to prevent moisture-related degradation.











































 HOME
HOME