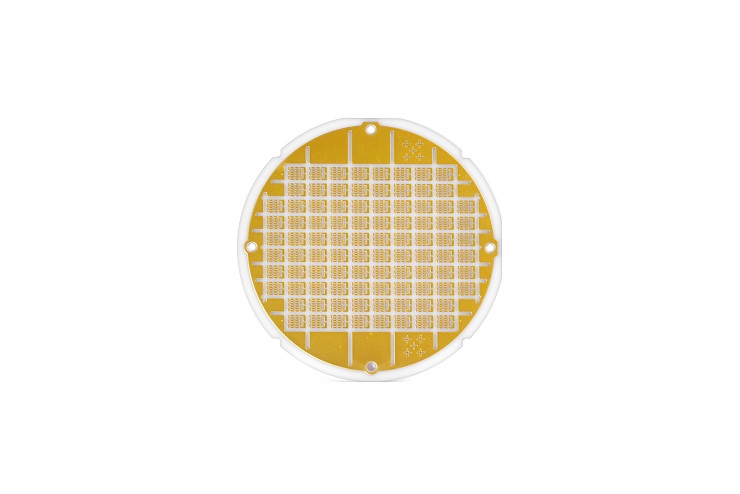
High quality DPC ceramic substrate for Micro Coolers
What Is Ceramic Substrate?
A ceramic substrate is an inorganic, non-metallic base material used to support and interconnect electronic components. It combines high thermal conductivity with excellent electrical insulation, dimensional stability, and mechanical strength. These characteristics make ceramic substrates ideal for high-performance applications, especially where effective heat dissipation is essential.
Unlike traditional organic PCBs (such as FR4), ceramic substrates do not degrade at high temperatures and are more stable across a wide range of environmental conditions. This makes them especially useful in areas such as power electronics, RF systems, automotive control units, medical devices, and micro cooling modules.
Types of Ceramic Substrate
Not all ceramic substrates are the same. Each type has its own strengths. Selecting the right ceramic material is critical in PCB design, especially when thermal and electrical performance are key. Below are the most commonly used ceramic substrates in electronic packaging:
1. Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina is the most widely used ceramic material due to its excellent cost-performance ratio. It offers moderate thermal conductivity (~20–25 W/m·K), good mechanical properties, and strong electrical insulation. It is suitable for many general-purpose applications.
2. Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
Aluminum nitride stands out for its superior thermal conductivity (up to 170–200 W/m·K) and electrical insulation. It is commonly used in high-power modules, micro coolers, and LED applications where efficient heat removal is critical.
3. Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
Known for high mechanical strength and thermal shock resistance, silicon nitride is often used in harsh environments such as automotive and aerospace. While its thermal conductivity is lower than AlN, its toughness makes it ideal for demanding mechanical applications.
4. DPC Ceramic Substrate (Direct Plated Copper)
DPC substrates feature a thin copper layer directly plated onto the ceramic surface, using laser activation and electroless plating techniques. This method allows for excellent thermal conductivity, strong adhesion, and fine pattern resolution—especially valuable for micro cooling solutions.
Advantages of DPC Ceramic PCB
DPC, or Direct Plated Copper, is a popular ceramic PCB process where copper is bonded directly onto ceramic materials. The DPC process uses laser direct structuring to create precise copper patterns without the need for etching or screen printing. This brings several advantages:
1. High-Precision Circuit Fabrication
DPC ceramic circuit boards use advanced semiconductor microfabrication technologies such as sputtering, photolithography, and developing. These techniques enable extremely fine metal traces on the ceramic substrate, achieving line widths and spacing as small as 30μm–50μm. The surface is also exceptionally flat, making it ideal for high-precision microelectronic packaging.
2. Vertical Interconnection Capability
By applying laser drilling and electroplated via-filling, DPC ceramic boards achieve vertical interconnection between the top and bottom layers of the ceramic substrate. This helps reduce device size, increase packaging density, and meet the growing demands for miniaturization and performance in modern electronic devices.
3. Outstanding Thermal Performance
The ceramic materials used in DPC substrates, such as aluminum nitride (AlN), offer high thermal conductivity. For instance, AlN has a theoretical thermal conductivity of up to 320 W/(m·K), which effectively reduces the operating temperature of electronic components and enhances stability and lifespan.
4. Low-Temperature Manufacturing Process
The DPC process operates at relatively low temperatures, typically below 300°C. This avoids damage to the substrate and metal layers caused by high temperatures, reduces production costs, and improves overall manufacturing efficiency.
5. Environmental Friendliness
Although the DPC process involves electroplating, it is more environmentally friendly compared to many traditional packaging materials. With ongoing improvements in waste treatment and recycling of plating solutions, its environmental impact continues to decrease.
Why DPC Ceramic PCB Is Suitable for Micro Coolers?
Micro coolers are compact thermal management solutions designed to regulate heat in high-density electronic devices such as lasers, power LEDs, semiconductor packages, and RF amplifiers. These applications demand fast heat dissipation, small size, and long-term reliability—requirements that match perfectly with the characteristics of DPC ceramic PCBs.
1. Miniaturization Without Performance Loss
As micro coolers get smaller, the heat they need to manage often increases. DPC ceramic substrates allow engineers to design compact PCBs with high thermal conductivity and precise copper patterns. This combination helps maintain performance even in tight spaces.
2. Excellent Heat Spreading
In micro coolers, it's essential to spread heat across the ceramic layer quickly to avoid hotspots. With DPC on AlN or Al₂O₃, the thermal resistance is extremely low. This helps achieve uniform heat dissipation and longer component life.
3. Superior Dielectric Strength
Because ceramic has high electrical insulation, DPC substrates can carry high voltages without risk of breakdown. This is vital in applications such as power lasers or RF power devices that require robust electrical isolation.
4. Reliable Metallization in Harsh Environments
Micro coolers often work in industrial or aerospace environments with wide temperature swings and vibration. The DPC process creates a strong, stable copper bond to the ceramic base, reducing the risk of failure due to stress or thermal expansion mismatch.
5. Direct Chip Attachment (DCA) Capability
DPC substrates allow for direct bonding of semiconductor chips thanks to their flat surface, high thermal performance, and strong copper adhesion. This minimizes interconnect resistance and boosts thermal conduction—key benefits for thermal modules in micro cooling applications.
Our Case Studies
At BstCeramic PCB, we’ve provided DPC ceramic solutions for various micro cooler applications across the electronics and photonics industries. Here are a few highlights:
Case Study 1: High-Power Laser Diode Micro Cooler
A client in the photonics industry needed a substrate for their high-power laser module. The challenge was to handle up to 100W of heat within a confined space. We recommended an AlN DPC substrate with 50μm copper thickness and custom layout. The final product delivered a 30% improvement in thermal performance and significantly extended the diode's lifetime.
Case Study 2: Medical Imaging Sensor Cooling Module
For a medical customer designing a high-resolution imaging sensor, temperature control was crucial. We provided a DPC ceramic PCB with multi-layer copper interconnects on alumina, enabling fine routing while maintaining heat management. The sensor operated within safe temperature ranges even during continuous use.
Case Study 3: Telecom RF Module Micro Cooler
A telecom company approached us with a need to integrate a high-frequency RF amplifier with a thermal control solution. The space was tight, and performance needed to be stable up to 80°C ambient. Our AlN-based DPC substrate supported both the thermal and electrical demands, resulting in 20% better performance and fewer system failures.
Your Reliable Ceramic PCB Manufacturer | BstCeramic PCB
BstCeramic PCB, a division of Best Technology, specializes in manufacturing high-quality DPC ceramic substrates tailored for thermal management applications like micro coolers. With over 18 years of PCB industry experience, we are trusted by clients across the medical, aerospace, telecom, and industrial sectors. Why choose us?
- Materials Variety: Alumina, Aluminum Nitride, and other ceramics.
- Certified Quality: ISO9001, ISO13485, AS9100D, IATF16949
- Custom DPC Process: Laser structuring, electroless copper plating, and thick copper capabilities.
- Engineering Support: Our engineers work with you to design the optimal substrate layout.
- Fast Turnaround: Efficient production lines backed by MES system traceability and quality tracking.
Whether you’re building a compact laser module, thermal imaging device, or RF amplifier with strict cooling needs, our team is here to help. From prototyping to mass production, we offer end-to-end support and quality that matches your performance standards.
If you're looking for a reliable partner to supply ceramic PCBs for thermal-critical projects, BstCeramic PCB is ready to deliver. We offer engineering support, material expertise, and precise fabrication to meet your demands—no matter how complex.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between DPC and other ceramic PCB types?
DPC uses laser structuring and electroless plating to directly bond copper onto ceramic. It offers higher precision and stronger copper adhesion than screen printing or thick film methods.
2. Why is AlN preferred over alumina for micro coolers?
AlN has higher thermal conductivity (~170 W/m·K) compared to alumina (~25 W/m·K), which makes it more effective in fast heat transfer applications like micro cooling systems.
3. Can I get custom copper thickness on DPC ceramic PCBs?
Yes. We can produce DPC PCBs with copper thickness from 10μm up to 300μm, depending on your thermal and electrical needs.
4. Is DPC ceramic substrate suitable for high-frequency applications?
Absolutely. DPC ceramic PCBs provide stable dielectric performance and low loss, making them great for RF and microwave circuits.
5. How do I request a quote for a custom DPC ceramic PCB?
You can contact us at sales@bstceramicpcb.com with your Gerber files, design requirements, and specifications. Our engineers will review your needs and respond with a competitive quote.











































 HOME
HOME