Is Alumina Ceramic Durable?
Yes, alumina ceramic is exceptionally durable.
It doesn’t bend or deform easily under stress, which is why it’s often used in high-load applications like mechanical seals, valve components, and precision bearings. Chemically, it resists corrosion from acids, alkalis, and solvents. And unlike polymers or some metals, alumina doesn’t oxidize or age poorly. Its durability comes not only from how hard or heat-resistant it is—but from how stable it stays over time.
What is Alumina Ceramic?
Alumina ceramic, also called aluminum oxide ceramic, is a high-performance material used in many technical and industrial fields. It is created by refining bauxite ore into aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), then shaping and sintering it under very high heat. The result is a dense, rigid ceramic that can handle mechanical stress, extreme temperatures, and chemical exposure.
Unlike traditional ceramics, alumina ceramic is not fragile in the same way. It combines mechanical strength with electrical insulation and thermal stability. Because of this, it is widely used in electronics, medical devices, automotive parts, and even aerospace components. It performs reliably in environments where plastic, metal, or standard ceramic would fail.
Alumina ceramic is available in different purities—typically 95%, 96%, 99%, and 99.5%, 99.6%. The higher the purity, the better the material performs in demanding applications. High-purity alumina is particularly suited for cleanroom and semiconductor use, where contaminants must be kept to a minimum. But higher purity also means the higher price.
Alumina Ceramic Physical Properties
|
Color |
White |
|
Molecular weight |
101.96 |
|
Melting point |
2054C |
|
Boiling point |
2980C |
|
Density |
3.97g/cm3 |
|
Crystal structure |
Hex |
|
Solvability |
Insoluble in water at room temperature |
|
Electric conductivity |
Not conduct electricity at normal temperature |
|
Crystal type |
Ionic crystal |
|
Thermochemical properties |
ΔfHθ(l)=1620.57kJ/mol ΔfHθ(s)=1675.69kJ/mol Sθ(l)=67.24J/mol·K(1bar) Sθ(s)=50.9J/mol·K |
Features of Alumina Ceramic
- High hardness to resist scratches, dents, and wear from repeated use or contact with other materials.
- Excellent electrical insulation, which means it blocks electricity from passing through.
- High thermal stability, performs well at high temp – often up to 1600C
- Good chemical resistance, and not affected by most acids, alkalis, or solvents.
- Non-magnetic, good to use in communication devices or precision instruments.
- It doesn’t expand or contract much with temperature changes
Alumina Ceramic Composition
The main component of alumina ceramic is aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃). The purity level of this oxide can range from 85% to over 99.9%, depending on the application requirements. Standard industrial-grade alumina ceramics are usually 95% to 96% pure. These grades are strong and economical, suitable for mechanical parts, insulating tubes, and protective coatings.
For more sensitive applications, such as semiconductor components, high-voltage insulators, and laser housings, 99.5% or higher purity alumina is used. These materials have fewer impurities, better thermal conductivity, and greater electrical resistance.
Other additives like zirconium oxide or magnesium oxide may be included in small amounts. These improve sintering during manufacturing and enhance toughness or grain size control. However, the base structure is always dominated by aluminum oxide.
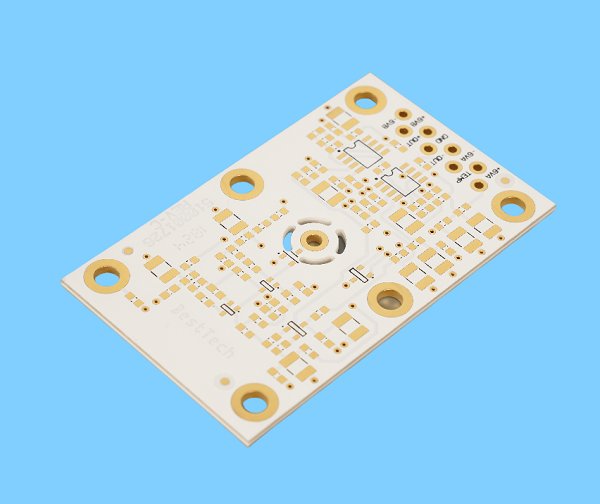
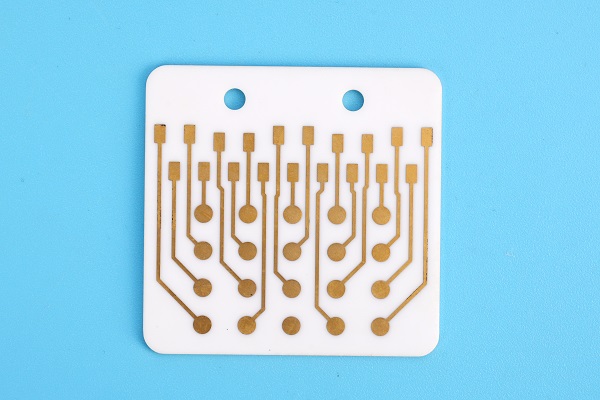
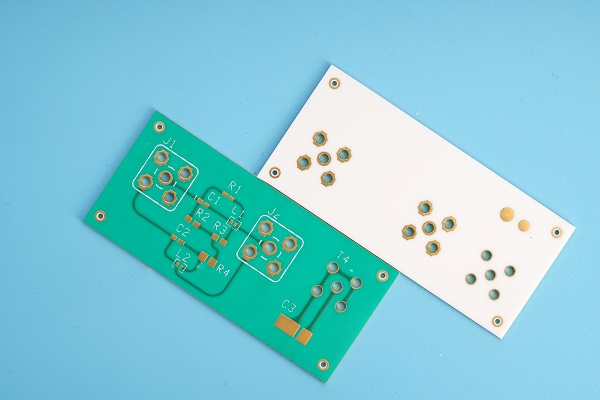
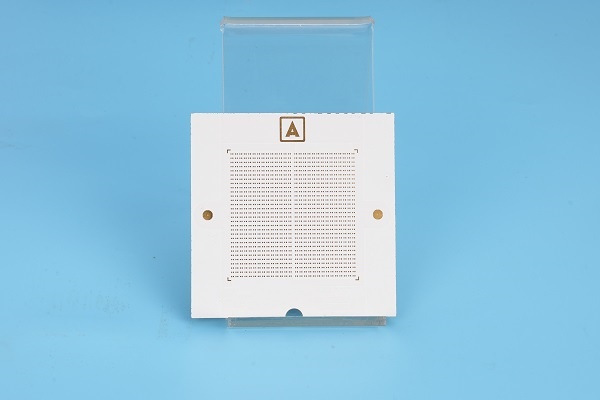
Alumina Ceramic PCB Products
Alumina ceramic is widely used in the PCB industry, especially for ceramic circuit boards. These boards are used when high heat resistance, strong electrical insulation, and long service life are required. Here are some alumina ceramic PCB products that made by Best Technology:
What is Alumina Ceramic Hardness?
Alumina ceramic is one of the hardest technical ceramics available. On the Mohs scale, which ranks materials by their scratch resistance, alumina scores between 8 and 9. For comparison, diamond ranks at 10. The high hardness makes alumina ceramic ideal for applications that require wear resistance. For example:
- Bearing sleeves
- Pump plungers
- Valve seats
- Cutting blades
It is also used in tools that need to maintain sharp edges or smooth surfaces over time.
In Vickers hardness testing, a common lab method for measuring hardness, alumina typically shows values over 1800 HV. This confirms its resistance to indentation and abrasion. Because it’s so hard, alumina doesn’t deform like metal under stress. It maintains its shape and size, which is important in precision engineering.
Alumina Ceramic Thermal Conductivity
Although alumina is an electrical insulator, it still conducts heat fairly well for a ceramic. Alumina ceramic thermal conductivity usually ranges from 20 to 30 W/m·K depending on the purity and grain structure.
This is lower than copper metals but much better than plastics or standard ceramics. In electronics, alumina helps remove heat from sensitive components. It spreads heat across the surface and away from hotspots, which prevents overheating and extends the lifespan of the device. Because it does not require additional cooling layers, alumina also helps reduce system size and weight.
Alumina Ceramic Uses
Alumina ceramic is used in a wide range of industries. Its combination of hardness, heat resistance, and electrical insulation makes it a valuable material for many applications.
- Medical field:
Dental crowns and implants
Hip and knee joint replacements
Surgical instruments and diagnostic tools
Alumina is biocompatible, so it doesn’t cause reactions in the body. It’s also sterilizable and holds up well inside the human body over long periods.
- Electronics industry:
Substrates for semiconductors
Laser diodes and LED modules
Resistors, capacitors, and sensors
- Automotive and aerospace:
Spark plug insulators
Exhaust system sensors
Radar and communication equipment
In these industries, the material faces extreme conditions but still performs reliably.
- Industrial machinery:
Sealing components in pumps and compressors
Guide rails and nozzles in high-wear environments
Protective linings for processing equipment
These parts benefit from alumina’s wear resistance and chemical strength, especially in settings involving high friction or corrosive substances.
- Defense and security:
Lightweight armor plates
Sensor housings
High-precision optical components
Its high hardness makes it effective at stopping impact and protecting sensitive devices.
Alumina Ceramic Substrate vs. Ceramic PCB
The terms can get confusing, but they’re not interchangeable.
Definition and use
- Alumina ceramic substrates are raw materials—thin plates of sintered ceramic used a foundation for circuits. They're passive, serving as platforms for building layers of conductive traces, often using screen printing or sputtering.
- Alumina ceramic circuit board usually refers to etching various patterns on a ceramic substrate to form a circuit connection, they are finished products. They include the substrate but add metallization, protective coatings, and functional circuit paths. It not only has the advantages of alumina ceramic substrates, but also can make complex circuit patterns on the ceramic surface. It is suitable for electronic equipment that requires high reliability and high temperature resistance.
Manufacturing process
- Alumina ceramic substrate: During the manufacturing process, copper foil and alumina
ceramic substrate are bonded together in a high temperature environment. This combination method prevents the copper foil from falling off, has high reliability, and is suitable for use in high temperature and high humidity environments.
- Alumina ceramic circuit board: During the manufacturing process, the alumina ceramic
substrate is first produced, and then the required circuit pattern is produced on its surface through processes such as sputtering and etching. This process enables the ceramic circuit board to achieve complex circuit design while maintaining the advantages of the ceramic substrate.
If you are interested in DPC Alumina ceramic PCB or alumina ceramic substrate, welcome to contact us at sales@bstceramicpcb.com.











































 HOME
HOME