Is Alumina Conductive or Not?
If you’re working with electronics or considering materials for high-performance PCBs, you might be wondering, “Is alumina conductive or not?” The short answer is no, alumina is not conductive. In fact, it’s well-known for being an excellent electrical insulator, which is exactly why it’s used in many electronic, electrical, and industrial applications.
In this guide, we’ll explain why alumina doesn’t conduct electricity, how it behaves in electronic environments, and why it’s a popular choice for ceramic PCBs.

Why Is Alumina a Bad Conductor of Electricity?
Alumina (also called aluminum oxide, with the chemical formula Al₂O₃) is a ceramic material made by oxidizing aluminum. What’s interesting about alumina is that although aluminum is a metal and conducts electricity very well, alumina does the opposite—it resists the flow of electric current.
The reason alumina is a poor conductor of electricity lies in its atomic structure. In alumina, aluminum and oxygen atoms are bonded tightly in a crystal-like formation. This strong bond traps electrons and prevents them from moving freely. In order for a material to conduct electricity, it must have free electrons or ions that can move through the material. Alumina has neither. Because of this, alumina’s electrical conductivity is extremely low—so low that it is considered an electrical insulator.
Is Alumina a Good Insulator?
Yes, alumina is not only a bad conductor—it’s actually one of the best insulators used in modern electronics. It can withstand very high voltages without breaking down or allowing current to pass through. Additional benefits of alumina insulators:
- Thermal stability: Alumina retains its insulating properties even at very high temperatures.
- Chemical resistance: It doesn’t degrade easily when exposed to moisture, chemicals, or corrosion.
- Mechanical strength: Alumina is hard and durable, making it suitable for demanding industrial environments.
Because of these characteristics, alumina is used in electrical insulators, spark plug insulators, and substrates for high-frequency circuits.

Alumina Relative Permittivity
Relative permittivity refers to how much electrical energy a material can store when it’s placed in an electric field. In simple terms, it tells us how well a material can act as a dielectric—a substance that stores electrical energy without conducting electricity.
For alumina, the relative permittivity ranges between 9 and 10. This is considered quite high and shows that alumina can store electrical energy effectively, which is crucial in the design of capacitors, antennas, and high-frequency applications.
A higher dielectric constant allows components to be smaller without losing energy storage capacity. That’s why alumina is often used in miniaturized electronics that need to remain efficient and reliable.
Is Alumina a Dielectric Material?
Yes, alumina is a dielectric material, and it performs exceptionally well in this role.
A dielectric is any material that does not conduct electricity but can polarize in the presence of an electric field. This means alumina can store electrical energy, which is especially useful in capacitors and PCB substrates. Alumina’s high dielectric strength, low dielectric loss, and stable performance over a wide temperature range make it a preferred dielectric material for many industries, including:
- Telecommunications
- Medical devices
- Automotive electronics
- LED lighting
- RF and microwave components
Is There a Difference Between Aluminum and Alumina?
Yes, there is a big difference between aluminum and alumina, even though their names sound similar.
Aluminum is a metallic element with the chemical symbol “Al”. It has excellent electrical conductivity and ductility, and is commonly used in the manufacture of aircraft, automobiles, and packaging materials, etc. For instance, the aluminum foil we use daily is made of aluminum.
However, alumina is an oxide of aluminum, with the chemical formula “Al₂O₃”. It is a white solid with high hardness and heat resistance, and is widely used in ceramics, refractory materials, and the electronics industry. For instance, the protective layer of mobile phone screens often uses alumina to enhance its wear resistance. Here is a detailed comparison between two of them:
|
Property |
Aluminum |
Alumina |
|
Type |
Metal |
Ceramic |
|
Conductivity (Electrical) |
~3.77 × 10⁷ S/m |
~10⁻¹² to 10⁻¹⁴ S/m (Insulator) |
|
Conductivity (Thermal) |
~205 W/m·K |
24–30 W/m·K |
|
Melting Point |
660.3°C |
2072°C |
|
Density |
2.70 g/cm³ |
3.9–4.0 g/cm³ |
|
Strength |
90–400 MPa |
2000–4000 MPa |
|
Hardness |
15–30 HB |
15–20 GPa (Vickers) |
|
Color |
Silvery |
White/off-white |
|
Corrosion Resistance |
Moderate |
Excellent |
|
Applications |
Wiring, frames, heat sinks |
PCBs, insulators, medical tools |
|
Cost |
Low |
Medium to High |
|
Recyclability |
High |
Low |
Why Use Alumina as Ceramic PCB Substrate?
Alumina is widely used in ceramic PCB substrates for several important reasons:
- Electrical Insulation: It prevents electrical current from leaking between components, protecting circuits from short circuits and electrical noise.
- Thermal Conductivity: Alumina helps dissipate heat effectively, reducing the risk of overheating in high-power applications.
- Mechanical Durability: It’s hard, scratch-resistant, and wear-resistant, which makes it suitable for rugged environments.
- Chemical Stability: It resists moisture, chemicals, and corrosion, extending the lifespan of the PCB.
- Miniaturization: High dielectric constant allows for compact, high-density circuit designs.
Because of these benefits, alumina is a top choice for LED PCBs, automotive sensors, power modules, and RF/microwave circuits.
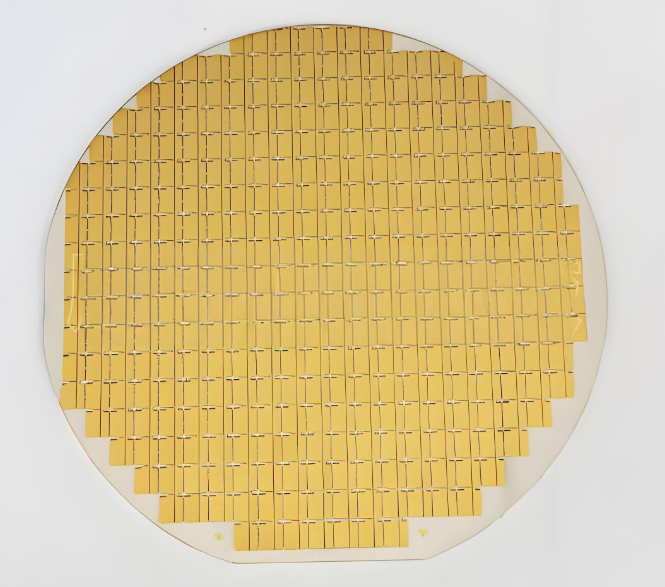
How Long Does Alumina PCB Last?
Alumina PCBs are known for their long service life. When properly designed and manufactured, an alumina PCB can last 10 to 20 years or more, depending on the application.
- High mechanical strength reduces the risk of cracking or breaking.
- Excellent heat resistance prevents thermal damage during operation.
- Corrosion resistance ensures stability in harsh environments.
- Stable electrical properties remain unchanged over time.
BstCeramicPCB’s Alumina Ceramic PCB Capability
At BstCeramic PCB, we are proud to offer premium alumina ceramic PCBs with a focus on precision, quality, and customization. Here’s what we can provide:
- Purity Options: We offer alumina substrates with 96% to 99.6% purity, suitable for various industries from consumer electronics to medical devices.
- Thickness Options: Standard thickness ranges from 0.25mm to 1.5mm, with custom sizes available.
- Circuit Patterning: Support for fine lines, high-density layouts, and multiple layers.
- Surface Finishes: Choices include silver, gold, ENIG, and other metal coatings to fit your design needs.
- Advanced Equipment: We use laser cutting, screen printing, and CNC milling to ensure precision and repeatability.
- Certification: Our facility is certified with ISO9001, ISO13485, AS9100D and IATF16949.
In addition to alumina ceramic PCB, we provide AlN ceramic PCB, BeO ceramic PCB and Si3N4 ceramic PCB. Here is our capability:
FAQs
1. Can alumina conduct heat but not electricity?
Yes, alumina conducts heat moderately well but is an excellent electrical insulator, making it perfect for heat management in electronics.
2. What is the dielectric strength of alumina?
Alumina’s dielectric strength ranges from 10 to 20 kV/mm, which helps it withstand high voltages without failure.
3. What temperature can alumina withstand?
Alumina remains stable at temperatures up to 1600°C, depending on purity, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
4. Is alumina safe for medical electronics?
Yes, high-purity alumina is biocompatible and used in medical devices, such as implants and diagnostic equipment.
5. Can alumina PCBs be customized?
Absolutely. At BstCeramic PCB, we offer custom alumina PCBs to match your specific requirements in layout, thickness, finish, and size.











































 HOME
HOME