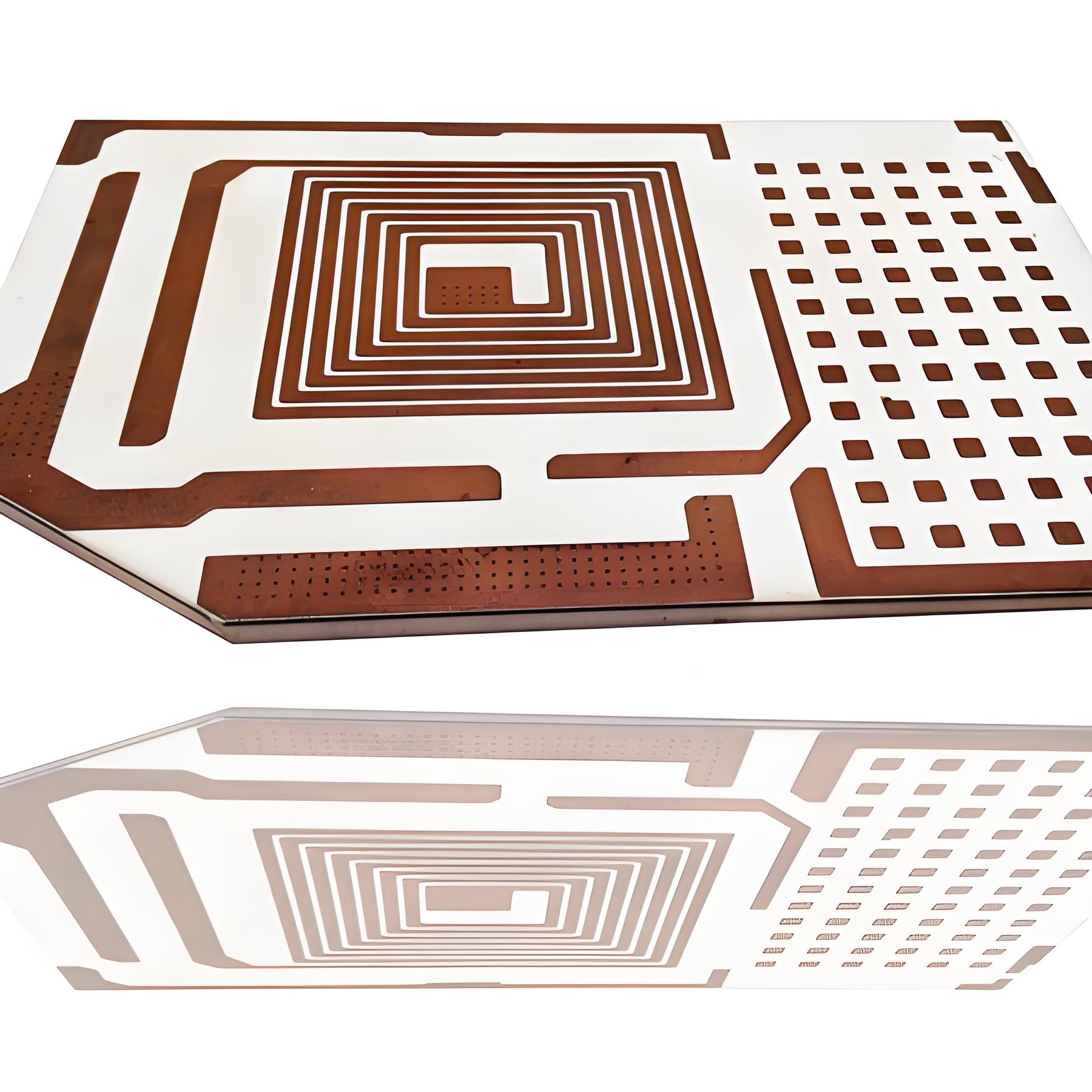
What is Alumina PCB Material? Alumina to Aluminium Process
What is Alumina PCB Material?
Alumina PCB is a ceramic-based printed circuit board that relies on aluminum oxide as its substrate. Unlike traditional FR4 boards, alumina PCB material offers outstanding thermal conductivity, excellent mechanical strength, and high electrical insulation. This combination allows it to work under extreme temperatures, heavy loads, and harsh environments where organic substrates fail.
Engineers often choose alumina circuit boards for applications where reliability is non-negotiable, such as automotive electronics, aerospace modules, medical implants, and LED lighting. These boards perform consistently under stress, maintaining stable functionality even in continuous high-power conditions.
The demand for alumina PCB is growing because industries now require compact designs that can handle heat efficiently without sacrificing lifespan. Whether used in sensors, RF devices, or laser equipment, alumina substrate PCBs deliver a balance of strength, safety, and long-term durability.
Alumina Chemical Composition
Alumina, chemically known as aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), consists of aluminum and oxygen atoms arranged in a crystalline lattice. This strong ionic structure contributes to its hardness, resistance to wear, and impressive dielectric properties.
The purity of alumina influences its performance. Common grades include:
- 90–95% alumina: Used in applications where moderate insulation and cost efficiency are prioritized.
- 96% alumina: A standard choice for alumina PCB substrate, offering good strength, electrical insulation, and cost balance.
- 99%–99.6% alumina: High-purity ceramics with superior resistance to chemical corrosion and higher dielectric strength, often used in medical devices, aerospace, and RF communication systems.
In the PCB world, the alumina chemical composition directly impacts signal quality, thermal conductivity, and mechanical endurance. High-purity alumina substrates reduce energy loss, making them ideal for high-frequency circuits.
Types of Alumina PCB Substrate
Different projects require different grades of alumina substrate PCB. Manufacturers typically provide several options:
- 96% Alumina PCB Substrate
This is the most commonly used type. It strikes a balance between price and functionality, suitable for LED PCBs, consumer electronics, and mid-level industrial devices.
- 99% Alumina Substrate PCB
This grade offers higher purity, leading to stronger electrical insulation and improved chemical resistance. It is often selected for aerospace electronics, automotive sensors, and high-power modules.
- 99.6% Alumina PCB Substrate
This premium material is the gold standard for industries like defense, high-frequency communication, and medical implants. It provides excellent dielectric properties and ensures minimal energy loss.
When selecting a type, designers consider thermal load, mechanical stress, and budget. An experienced alumina PCB manufacturer guides clients in choosing the right substrate to maximize performance.

How Much Does Aluminum PCB Cost?
Alumina PCB price varies widely, depending on several factors:
- Material Purity: High-purity grades like 99.6% alumina are more expensive than 96% alumina.
- Board Thickness: Thicker boards cost more due to higher material usage.
- Design Complexity: Multi-layered or fine-pitch designs increase fabrication cost.
- Order Volume: Bulk orders lower the per-unit price.
On average, alumina PCB price is higher than FR4 boards, but this cost reflects enhanced reliability and longer lifespan. For instance, LED manufacturers may pay more upfront for alumina PCB material, yet benefit from fewer failures and reduced maintenance costs over time.
It is important to distinguish between activated alumina price and alumina PCB cost. Activated alumina is used in water treatment and filtration, not electronics. For electronics, customers should request a detailed quote from an alumina PCB manufacturer that includes processing, substrate grade, and testing fees.
How Thick is Alumina PCB?
The thickness of alumina PCBs typically ranges from 0.25 mm to 1.5 mm. However, custom thicknesses are available for specialized projects.
- Thin Substrates (0.25–0.5 mm): Commonly used in compact devices like sensors, RF modules, and medical electronics.
- Standard Thickness (0.6–1.0 mm): Ideal for LED lighting boards and automotive electronics.
- Thicker Substrates (1.0–1.5 mm or more): Used in high-power electronics where thermal dissipation is critical.
Thicker alumina circuit boards absorb and spread heat more effectively, preventing hotspots that could damage components. Designers must carefully balance thickness, weight, and performance requirements when choosing the substrate.
Why is Alumina So Hard?
Alumina is among the hardest ceramic materials, ranking 9 on the Mohs scale, just below diamond. Its hardness is the result of strong ionic bonds between aluminum and oxygen atoms, which form a stable crystal lattice.
This hardness benefits electronics in several ways:
- Prevents scratches or surface wear.
- Ensures mechanical stability under pressure.
- Supports long-term reliability in devices exposed to vibration or shock.
For alumina PCB substrates, this property means boards remain dimensionally stable even after years of use. Unlike organic laminates, alumina does not warp, crack, or degrade easily, making it an excellent choice for mission-critical electronics.

Is Alumina the Same Thing as Aluminum?
No, alumina and aluminum are not the same. Alumina (Al₂O₃) is a chemical compound, while aluminum is a pure metal. The alumina to aluminium process transforms alumina into metallic aluminum through refining and smelting.
In PCBs:
- Alumina PCB Material: Provides electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and heat resistance.
- Aluminum PCBs: Use a metallic aluminum base with dielectric layers for thermal management.
While both materials relate to aluminum, their applications differ. Engineers should distinguish between alumina substrate PCB (ceramic-based) and aluminum PCBs (metal-core) when selecting materials for their projects.
How Long Does Alumina Last?
Alumina’s durability is one of its strongest advantages. It does not oxidize easily, resists chemical attack, and withstands extreme mechanical stress. In electronics, alumina PCB substrates can last for decades if operated within design parameters.
Factors that contribute to longevity include:
- Corrosion Resistance: Alumina does not rust or degrade in humid conditions.
- Wear Resistance: Its hardness prevents surface erosion.
- Thermal Stability: Operates consistently under high temperatures.
For industries like aerospace and automotive, this longevity reduces downtime and replacement costs. In many cases, the alumina circuit board will outlast the device itself.
Alumina to Aluminium Process
The transformation of alumina into aluminum involves two main stages:
- Bayer Process
Bauxite ore is refined into pure alumina by dissolving it in caustic soda at high temperature and pressure. This step separates impurities and produces alumina powder.
- Hall-Héroult Process
The purified alumina undergoes electrolysis, where it is reduced into metallic aluminum using carbon electrodes. This process requires significant energy but produces the lightweight, versatile aluminum used worldwide.
For PCB applications, however, the focus is not on metallic aluminum but rather on high-purity alumina ceramics. An alumina PCB manufacturer uses sintering and specialized ceramic processing to convert alumina into reliable PCB substrates.
Why Choose Best Technology as Your Alumina PCB Manufacturer?
Selecting the right manufacturer is crucial when working with alumina PCBs, and Best Technology stands out for several reasons. First, our facilities operate under strict quality standards with ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949, and AS9100D certifications, ensuring every board meets international expectations. We combine advanced ceramic processing with MES-controlled traceability, so every alumina substrate PCB is fully monitored from raw material to finished product.
Our engineering team provides professional consultation to help you select the ideal alumina grade, thickness, and design for your project. Whether your focus is thermal management, high-frequency performance, or mechanical durability, we guide you toward the best solution.
FAQs About Alumina PCB
1. What is basic alumina?
Basic alumina refers to aluminum oxide in its most common form, derived from bauxite ore. It is a stable compound with a crystalline structure used in ceramics, refractories, and electronic substrates.
2. What industries use alumina PCB?
Alumina circuit boards are widely used in LED lighting, automotive sensors, aerospace modules, medical devices, RF communication, and power electronics.
3. How does alumina PCB compare to FR4 PCB?
Alumina PCB provides higher thermal conductivity, better insulation, and longer lifespan compared to FR4 PCBs. However, FR4 is less costly and easier to process.
4. What is the difference between alumina substrate PCB and aluminum PCB?
Alumina substrate PCB uses ceramic alumina material for insulation and heat resistance, while aluminum PCBs rely on a metallic aluminum base with a dielectric layer.
5. Can alumina PCB be customized?
Yes. Thickness, purity, and design can be customized depending on the application. A professional alumina PCB manufacturer can tailor substrates to meet specific requirements.











































 HOME
HOME