What Is the Common Solder Mask Used on Thick Film Ceramic Substrates?
In the world of thick film ceramic PCBs, every layer counts. Among these layers, the solder mask, often referred to as glass glaze, plays a key role in protecting and insulating the circuit. Though it may look simple on the surface, this coating directly affects durability, heat resistance, and electrical performance.
Many engineers working with ceramic PCBs often ask what type of solder mask is used and how it differs from those found in standard FR4 boards. Let’s explore what makes glass glaze unique and why it’s the preferred choice for thick film ceramic substrates.
What Is the Solder Mask on Thick Film Ceramic Boards Called?
The solder mask used on thicsk film ceramic boards is generally called glass glaze. Unlike the organic solder mask seen on FR4 or flexible PCBs, glass glaze is an inorganic coating that bonds tightly to the ceramic surface during high-temperature firing.
This special material provides strong insulation, high hardness, and excellent thermal stability. It helps prevent oxidation, electrical leakage, and metal migration under continuous heating.
In simple terms, glass glaze acts as both a protective shield and an insulating layer for printed circuits on ceramic substrates.
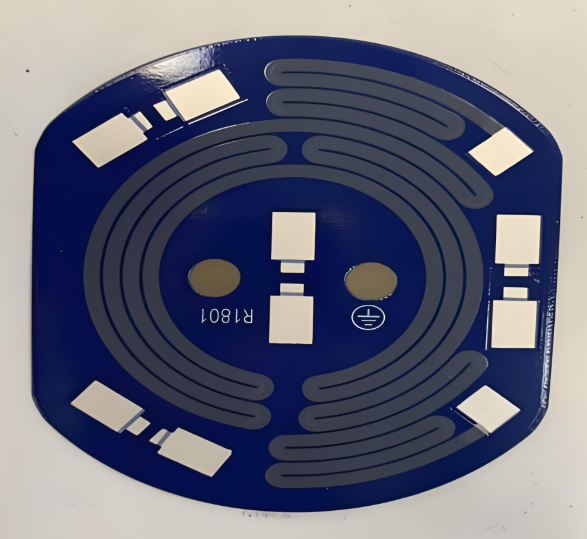
Why Is Glass Glaze Used Instead of Conventional Solder Mask?
Thick film ceramic PCBs are designed to handle high temperatures and harsh environments. Conventional epoxy-based solder masks cannot survive such conditions, as they tend to soften or discolor when exposed to extreme heat.
Glass glaze, on the other hand, can withstand firing temperatures above 500°C, maintaining its strength and adhesion even in demanding thermal cycles. This stability is essential for applications like power modules, automotive sensors, and high-frequency devices where thermal stress is a daily challenge.
What Are the Common Colors of Glass Glaze?
The most common colors for glass glaze used on thick film ceramic boards are blue and green.
- Green glass glaze is the traditional choice, known for its clean appearance and good contrast with silver or gold conductors.
- Blue glass glaze offers a brighter surface and is often selected for aesthetic or identification reasons, especially in optical or consumer products.
Although these two colors dominate, custom shades may be available depending on material supplier or end-use application.
How Is Glass Glaze Applied to Ceramic Boards?
The application process of glass glaze is precise and temperature-controlled. It usually involves:
- Screen Printing: A fine layer of glass paste is printed on the ceramic substrate to cover exposed areas.
- Drying: The coated board is heated gently to remove solvents and stabilize the glaze layer.
- Firing: The substrate is fired at high temperature, typically above 500°C, to fuse the glaze into a hard, durable surface.
The result is a smooth, glossy, and non-porous finish that resists moisture, chemicals, and electrical leakage.
Advantages of Glass Glaze Solder Mask
- High thermal endurance: It can resist extreme heat far beyond the capability of organic coatings.
- Excellent insulation: Prevents short circuits even under high voltage or moisture.
- Chemical stability: Resists corrosion from fluxes and cleaning agents.
- Durable finish: The fired surface is tough, smooth, and long-lasting.
How Does Glass Glaze Affect Circuit Appearance?
Besides protection, glass glaze gives ceramic boards a clean and professional appearance. The smooth blue or green coating covers unwanted conductor areas and highlights solder pads.
This not only improves visual inspection but also helps with optical recognition during assembly. The color also differentiates layers or product batches, aiding traceability in manufacturing.
Case of Applying Glass Glaze on Ceramic PCBs
At Best Technology, glass glaze is applied through a strict, multi-step process. After screen printing, each board undergoes precision drying and firing under controlled temperature profiles.
A customer in the automotive sector once required a high-voltage thick film substrate that could handle 250°C continuous operation. Best Technology selected a green glass glaze for its high insulation and low dielectric loss.
After reliability testing, the glaze maintained performance without cracking or discoloration, confirming its suitability for long-term use.
Why Work with Best Technology for Thick Film Ceramic Boards?
Best Technology specializes in thick film ceramic PCB manufacturing, including alumina and aluminum nitride substrates. We provide full process control from screen printing, glaze coating, to laser cutting and metallization.
Our facilities operate under ISO9001, IATF16949, ISO13485, and AS9100D certifications, ensuring high-quality production across industries. Using advanced MES traceability systems, every piece of material and process parameter is recorded for consistent quality control. Our engineers can also recommend suitable glass glaze materials based on your temperature and insulation requirements.
If you are developing thick film circuits or high-performance ceramic boards, Best Technology can help you select the best glass glaze and process to meet your goals.
FAQs
1. What is the solder mask on ceramic PCBs called?
It’s called glass glaze, an inorganic insulating layer fused onto the ceramic surface.
2. What colors are available for glass glaze?
The most common colors are blue and green.
3. Can glass glaze handle high temperatures?
Yes. It can withstand over 500°C during firing and remains stable in operation.
4. Why not use standard solder mask on ceramic boards?
Organic solder masks can’t tolerate the high firing temperatures or long-term heat exposure of ceramic substrates.
5. Can Best Technology customize the glass glaze color?
Yes. Depending on your application and material choice, custom colors can be developed upon request.











































 HOME
HOME