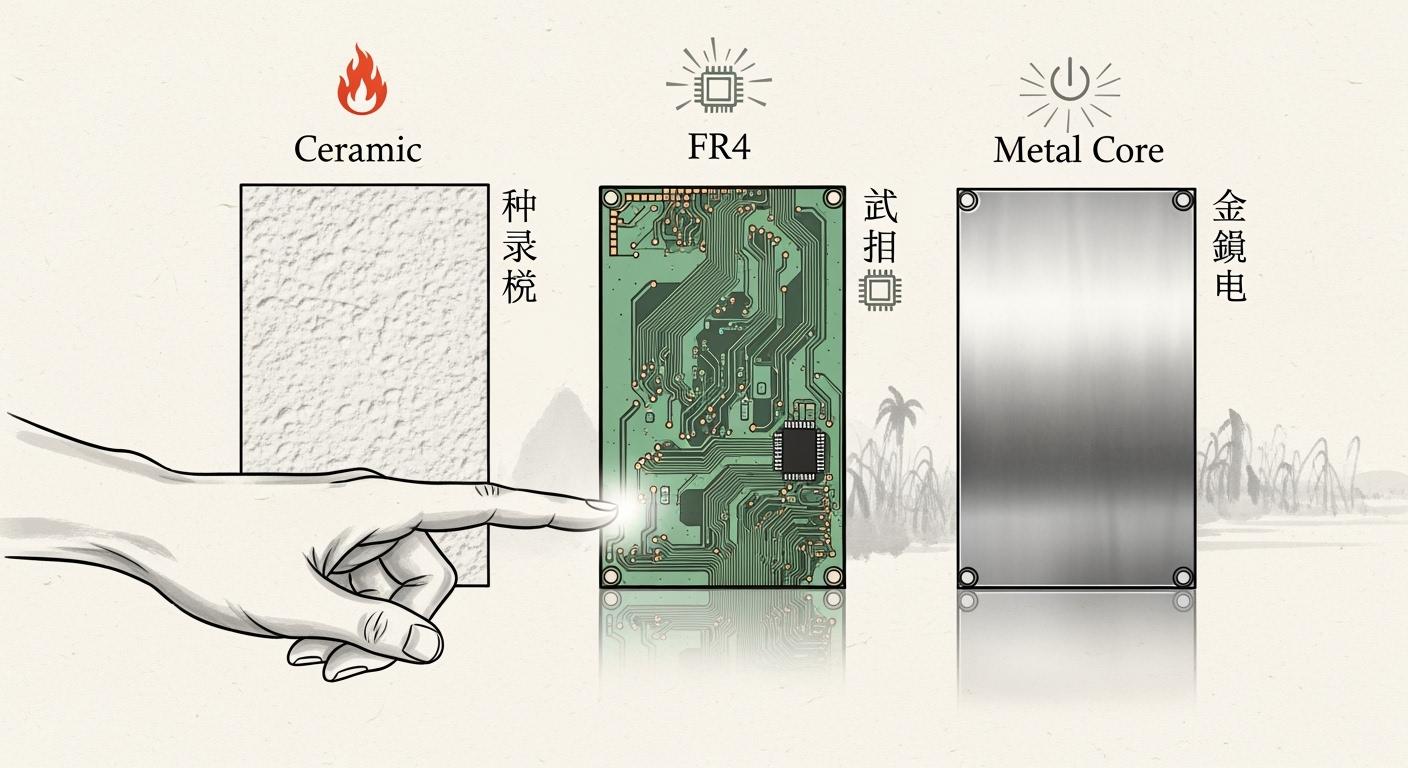
How to Choose Between Ceramic, FR4, and Metal Core PCBs
When you need to choose between ceramic pcbs, FR4, and metal core PCBs, you must consider several critical factors. Your application’s requirements will drive your decision. Most engineers focus on:
- Signal integrity—FR4 works well for rates below 5 Gbps, while higher speeds may need specialty materials.
- Thermal management—High power density or heat-sensitive parts often require metal core or ceramic solutions.
- Budget—FR4 fits cost-sensitive projects, but ceramic and metal core options suit specialized needs.
Each factor shapes your PCB selection process.
Key Takeaways
- Consider signal integrity when choosing PCBs. FR4 works well for speeds below 5 Gbps, while ceramic and metal core options suit higher speeds.
- Evaluate thermal management needs. Metal core and ceramic PCBs excel in heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-power applications.
- Balance your budget with performance requirements. FR4 is cost-effective for general use, while ceramic and metal core PCBs are better for specialized needs.
- Assess mechanical strength and durability. Choose ceramic for high-stress environments, while metal core PCBs resist vibration and shock.
- Use a selection checklist to guide your decision. Evaluate thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties to ensure the best fit for your project.
Quick Comparison of PCB Types
Key Selection Criteria
When you compare ceramic, fr4, and metal core PCBs, you should focus on several key criteria. These include material composition, thermal conductivity, cost, and typical applications. The table below gives you a clear overview:
| PCB Type | Material Composition | Thermal Conductivity | Typical Applications | Cost per Square Inch |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 | Flame retardant glass reinforced epoxy resin | Low | Consumer electronics | $5 - $15 |
| Ceramic | Aluminum oxide or aluminum nitride | High | High frequency and high power applications | $50 - $100 |
| MCPCB | Metal core with dielectric | Very High | LED and power devices | $10 - $25 |
You should consider how each type matches your project’s needs. For example, fr4 offers a cost-effective solution for most consumer electronics. Ceramic PCBs deliver high dielectric constant and low loss, which makes them ideal for high-frequency circuits. Metal core PCBs provide 5-10 times higher thermal conductivity than fr4, so they work well in high thermal load environments.
Tip: If your design requires excellent heat dissipation, you should look at metal core or ceramic options. For basic electronics, fr4 usually meets your requirements.
When to Use Each Type
You can use the following guidelines to decide which PCB fits your application:
- Choose fr4 for low-frequency, low-power devices such as smartphones, laptops, and home appliances.
- Select ceramic PCBs for high-frequency, high-power, or RF applications where signal integrity matters.
- Opt for metal core PCBs when you need superior thermal management, such as in LED lighting or power converters.
Ceramic PCBs excel in environments with high temperatures and demanding electrical performance. Metal core PCBs suit designs that generate significant heat. Fr4 remains the standard for most commercial electronics due to its balance of performance and affordability.
If you have a unique requirement or face uncertainty, you should reach out to a PCB expert or use a contact form to get tailored advice. Your choice will impact your device’s reliability and efficiency.
Ceramic PCBs Overview
What Is a Ceramic PCB?
You use a ceramic pcb when your design demands high performance in harsh or high-temperature environments. Ceramic pcbs use materials like alumina, aluminum nitride, or beryllium oxide instead of traditional fiberglass. These boards offer excellent electrical insulation and thermal conductivity. You often see thick film ceramic pcb and multilayer ceramic pcb options, which allow for complex circuit designs and high-density layouts.
Ceramic PCB Properties
Ceramic pcbs stand out because of their unique properties. The table below compares their characteristics to other PCB types:
| Characteristic | Ceramic PCBs | Other PCBs |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent | Varies |
| Electrical Insulation Properties | Strong | Varies |
| Mechanical Strength and Durability | High | Varies |
| Dielectric Loss | Low | Higher |
| Performance in High-Frequency Apps | Superior | Limited |
| Suitability for Harsh Environments | Ideal | Limited |
You find that ceramic pcbs use materials such as alumina for mechanical strength, aluminum nitride for high thermal conductivity, and beryllium oxide for extreme heat dissipation. These materials help you achieve reliable performance in demanding applications.
Advantages of Ceramic PCBs
Ceramic pcbs deliver several key benefits:
- Superior thermal management, which prevents overheating in compact spaces.
- Consistent electrical properties across a wide frequency range.
- Low dielectric loss, which improves signal integrity in high-frequency circuits.
- High mechanical strength, so your board resists warping and cracking.
- Reliable operation in harsh or rapidly changing environments.
You often select a thick film ceramic pcb for its ability to handle high power and maintain stability under stress.
Limitations of Ceramic PCBs
You should consider some limitations before choosing a ceramic pcb:
| Limitation | Description |
|---|---|
| Higher Costs | Ceramic pcbs cost more due to expensive materials and complex processes. |
| Brittleness | These boards can be more brittle, so they may crack if handled roughly. |
A thick film ceramic pcb offers great performance, but you must weigh the cost and handling requirements.
Best Uses for Ceramic PCBs
You see the application of ceramic pcb in industries where reliability and performance matter most:
- Aerospace and defense systems
- Medical imaging and diagnostic devices
- Automotive power modules and battery management
- LED lighting for heat-sensitive environments
- Power electronics and telecommunications
You choose a high temperature ceramic pcb for extreme heat, while a low temperature ceramic pcb suits less demanding conditions. The application of ceramic pcb often includes thick film ceramic pcb for power electronics and multilayer ceramic pcb for advanced communication systems.
If you need a PCB that can handle heat, high frequency, or harsh conditions, ceramic pcbs are your best option. For more details or to discuss your project, consider reaching out through our contact form.
FR4 PCB Basics
What Is FR4?
You encounter fr4 as the most common material for printed circuit boards. Fr4 stands for "Flame Retardant 4," which refers to its fire-resistant properties. You find fr4 boards made from a combination of glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin. The glass fiber cloth gives fr4 boards their mechanical strength and rigidity. The epoxy resin acts as a bonding agent and provides electrical insulation. Manufacturers typically laminate fr4 boards with a thin layer of copper foil, which forms the conductive traces.
- Glass fiber cloth: Delivers strength, rigidity, and stability.
- Epoxy resin: Offers insulation and flame resistance.
- Copper foil: Enables electrical connections.
FR4 Properties
Fr4 boards offer a balance of electrical, mechanical, and thermal properties. You benefit from their water resistance and dimensional stability. The structure insulates adjacent copper planes and maintains the integrity of your circuits. Fr4 boards provide the following key properties:
- Excellent electrical insulation
- Good mechanical strength
- Stable performance in moderate temperatures
- Resistance to moisture and chemicals
You can rely on fr4 boards for consistent results in many environments.
FR4 Pros and Cons
You should weigh the advantages and disadvantages of fr4 boards before making a decision. The table below summarizes the most important points:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Excellent electrical performance | Moisture sensitivity |
| Thermal stability | Limited frequency range |
| Mechanical strength | Thermal limitations |
| Cost-effectiveness | |
| Versatility in design |
Fr4 boards deliver strong electrical performance and mechanical durability. You also benefit from their cost-effectiveness and design flexibility. However, you may encounter issues with moisture sensitivity and limited performance at very high frequencies or extreme temperatures.
FR4 Applications
You see fr4 boards used in a wide range of industries. Fr4 boards appear in consumer electronics such as smartphones, computers, and home appliances. You also find fr4 boards in automotive electronics, industrial automation, communication equipment, LED lighting, and medical devices. Their versatility and reliability make fr4 boards a top choice for many engineers.
- Automotive electronics
- Industrial control and automation
- Consumer electronics
- Communication equipment
- LED lighting
- Medical electronics
Tip: If you need a reliable, cost-effective solution for most electronic devices, fr4 boards offer a proven foundation. For specialized needs, consider reaching out through our contact form to discuss your project requirements.
Metal Core PCB Guide

What Is a Metal Core PCB?
You use a metal core pcb when your design needs efficient heat dissipation and mechanical strength. Metal core printed circuit boards have a base layer made from metals such as aluminum, copper, or steel alloy. This metal base replaces the standard fiberglass core found in traditional PCBs. The metal layer helps transfer heat away from sensitive components, making these boards ideal for high-power and high-temperature applications.
Metal Core PCB Properties
Metal core pcbs stand out for their thermal and mechanical properties. The choice of metal affects performance. Aluminum offers a good balance between cost and thermal conductivity, while copper provides the highest heat transfer. Steel alloys add strength but have lower thermal conductivity.
| Metal | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
| Aluminum | 237 |
| Copper | 401 |
| Steel Alloy | 16 |
You can see that copper-based metal core printed circuit boards deliver the best heat dissipation, but aluminum remains popular due to its affordability and solid performance.
Metal Core PCB Advantages
You gain several benefits when you choose metal-core pcbs for your project:
- Superior heat dissipation keeps components cool and prevents thermal damage.
- High mechanical strength resists vibration, shock, and bending.
- Efficient thermal management allows you to use high-density and high-power circuits.
- Extended component lifespan, especially for LEDs and power devices.
- Reliable operation in harsh or demanding environments.
- Improved efficiency and stability in LED lighting and power electronics.
Note: Metal core pcb technology helps you maintain optimal performance and reliability, even in challenging conditions.
Metal Core PCB Limitations
You should also consider the limitations of metal core pcbs:
- Higher cost compared to standard FR4 boards, especially with copper cores.
- Increased weight due to the metal base, which may not suit all portable devices.
- Limited flexibility in multilayer designs, as the metal core can restrict certain layouts.
Despite these drawbacks, metal core printed circuit boards remain a top choice for applications where heat and durability matter most.
Metal Core PCB Applications
You find metal-core pcbs used across many industries. The table below highlights common applications:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| LED Lighting | Heat dissipation, brightness, and lifespan extension |
| Automotive Electronics | Power controllers, voltage regulators, ignition systems, EV drives |
| Power Electronics | DC-DC converters, solid-state relays |
| Consumer & Industrial Equipment | LCD backlighting, printers, medical monitoring equipment |
| Renewable Energy | Solar panels, photovoltaic systems, motion control systems |
You often select a metal core pcb for LED lighting, automotive power modules, and renewable energy systems. These boards help you manage heat, improve reliability, and extend the life of your products.
If you need help choosing the right metal core pcb for your application, consider reaching out through our contact form. Your project can benefit from expert guidance on thermal management and board selection.
PCB Type Comparison
Thermal Performance
You need to consider thermal performance when selecting a PCB for your project. Thermal conductivity measures how well a material transfers heat. This property affects how efficiently your board manages heat generated by components. High thermal conductivity ensures that heat moves away from sensitive parts, reducing the risk of failure.
The table below compares the thermal conductivity values for common PCB types:
| Type of PCB | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
| FR4 PCB | 0.3–0.4 |
| Aluminum PCB | 1–3 |
| Copper-core PCB | ~400 |
| Ceramic (Al₂O₃/AlN) PCB | 20–170 |
Ceramic pcbs offer high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for demanding applications. Copper-core PCBs deliver the highest thermal conductivity, but you may find them less common due to cost. Aluminum PCBs provide a balance between cost and high thermal conductivity. FR4 PCBs have low thermal conductivity, which limits their use in high-power designs.
Tip: If your design involves high-power components or requires advanced thermal management, you should prioritize materials with high thermal conductivity.
Cost Factors
Cost plays a major role in your PCB selection. You must balance performance with budget constraints. The table below outlines typical cost ranges and key properties:
| Material | Cost per Sq. Ft. | Key Properties | Typical Applications | Cost-Saving Alternative |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | $1-$10 | Versatile, moderate thermal performance | Consumer electronics, prototyping | N/A |
| Aluminum | $10-$20 | High thermal conductivity | LED lighting, automotive | FR-4 with thermal vias |
| Ceramic | $50-$200 | Extreme thermal/electrical performance | Aerospace, medical devices | Aluminum or high-Tg FR-4 |
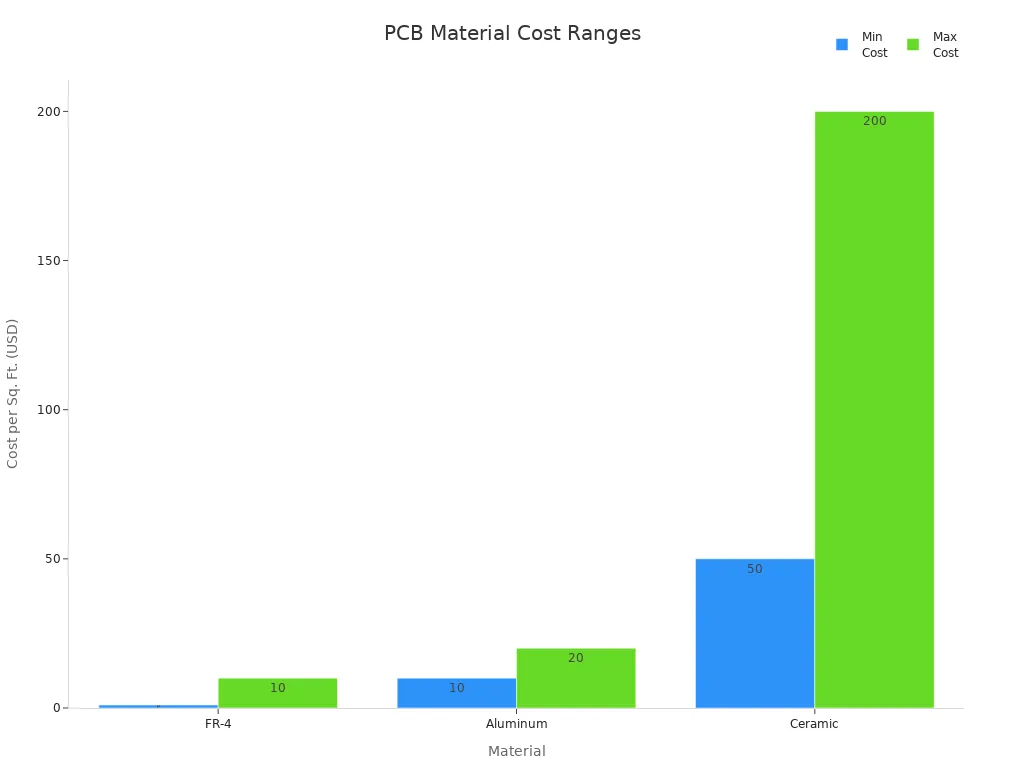
FR4 remains the most affordable option for general use. Aluminum PCBs cost more but deliver high thermal conductivity for better thermal management. Ceramic pcbs are the most expensive due to their specialized materials and processing requirements. You should choose ceramic only when your application demands extreme performance.
Note: You can reduce costs by using FR4 with thermal vias or high-Tg FR4 in place of aluminum or ceramic for moderate thermal management needs.
Mechanical Strength
Mechanical strength determines how well your PCB withstands physical stress, vibration, and shock. You need strong boards for automotive, aerospace, and industrial environments. Ceramic pcbs provide high mechanical strength but can be brittle. Metal core PCBs offer moderate strength and resist bending and vibration. FR4 PCBs deliver good strength for most consumer and industrial uses.
- Ceramic pcbs: High strength, but less flexible and more brittle.
- Metal core PCBs: Moderate strength, good resistance to vibration.
- FR4 PCBs: Reliable strength for general applications.
If your device faces frequent movement or impact, you should consider metal core or FR4 boards. Ceramic suits static, high-stress environments.
Design Complexity
Design complexity affects manufacturability and cost. You must evaluate how easily you can implement your pcb design and layout with each material.
- Ceramic pcbs require specialized manufacturing techniques. You may face limitations in multilayer designs and fine features.
- Metal core PCBs benefit from mature processes. You can achieve high-density layouts, but the metal base restricts some design options.
- FR4 PCBs offer the greatest flexibility. You can create complex multilayer boards and intricate pcb design and layout with standard processes.
Block Quote: You should select FR4 for complex designs unless your application demands high thermal conductivity or high-frequency performance.
Reliability and Environment
Reliability depends on how well your PCB performs in harsh conditions, such as high humidity, vibration, and temperature extremes. The table below summarizes environmental resistance:
| PCB Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Moisture Resistance | Vibration Resistance | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | 20-30 (Alumina), up to 170 (AlN) | Low (close to 0%) | Less than flexible | High-power applications like EV BMS |
| Metal-core | 1-10 (Aluminum) | Moderate | Moderate | LED headlight systems, powertrain controls |
| FR-4 | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | General use in moderate conditions |
Ceramic pcbs excel in reliability for high-power and high-temperature environments. Metal core PCBs perform well in moderate conditions and resist vibration. FR4 PCBs suit general use but may not withstand extreme environments.
Emoji:











































 HOME
HOME