Ceramic Circuit Board Material: Types, Properties, and How to Choose the Right One?
As power density, operating temperature, and reliability requirements continue to rise in modern electronics, ceramic circuit board material has become a preferred solution for high-performance applications. Compared with traditional FR-4, ceramic PCBs offer superior thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and long-term stability, making them ideal for automotive, aerospace, power electronics, and LED industries.
This guide explains what ceramic circuit board materials are, the most common ceramic PCB material types, their properties, metallization methods, failure causes, and how to choose a reliable ceramic PCB manufacturer.
What Is Ceramic Circuit Board Material?
Ceramic circuit board material refers to inorganic, non-metallic substrates used to fabricate printed circuit boards. Instead of epoxy glass laminates, ceramic PCBs use materials such as alumina or aluminum nitride, combined with copper or other metallization layers.
Key characteristics of ceramic PCB materials include:
- High thermal conductivity
- Excellent electrical insulation
- High temperature resistance
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
- Superior chemical and aging stability
Because of these properties, ceramic circuit boards are widely used in environments where conventional PCB materials fail.
What Applications Use Ceramic Circuit Board Material Most Often?
Ceramic substrates appear most frequently in designs where failure is not an option and thermal margins are narrow.
Typical applications include:
- Power modules for industrial drives and converters
- High-power LED lighting and UV systems
- Automotive electronics exposed to engine-bay temperatures
- RF and microwave circuits with tight signal stability requirements
- Aerospace and defense electronics
- High-voltage industrial control systems

In these environments, heat accumulation is the primary cause of premature failure. Ceramic circuit board material directly addresses this issue by transferring heat away from active components more efficiently than organic laminates.
How Does Ceramic Circuit Board Material Compare With FR4?
For most engineers, the decision begins with a comparison against FR4.
|
Parameter |
Ceramic Circuit Board Material |
FR4 PCB |
|
Thermal Conductivity |
20–340 W/m·K |
~0.3 W/m·K |
|
Maximum Operating Temperature |
>300°C |
130–170°C |
|
Dielectric Stability |
Excellent |
Moderate |
|
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
Low |
Higher |
|
Mechanical Behavior |
Rigid, brittle |
Flexible |
|
Cost |
Higher |
Lower |
FR4 is suitable for the majority of consumer and industrial electronics. However, once junction temperature, power density, or thermal cycling life become limiting factors, ceramic materials provide a decisive advantage.
The comparison is not about which material is “better,” but about which failure mechanism must be controlled.
What Types of Ceramic Circuit Board Material Are Commonly Used?
Different applications require different ceramic materials. Below are the most commonly used ceramic PCB substrates.
- Alumina (Al₂O₃)
- Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
- Beryllium Oxide (BeO)
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)

Alumina (Al₂O₃)
Alumina is the most widely used ceramic PCB material due to its balanced performance and cost.
96% Alumina (Al₂O₃)
- Thermal conductivity: ~24 W/m·K
- Dielectric strength: High
- Cost-effective
- Suitable for consumer electronics, industrial control, and standard power modules
99% Alumina (Al₂O₃)
- Thermal conductivity: ~28–30 W/m·K
- Higher purity and better insulation
- Improved mechanical strength
- Used in automotive electronics, medical devices, and telecom equipment
Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
Aluminum nitride is a premium ceramic circuit board material known for its outstanding thermal performance.
- Thermal conductivity: 170–230 W/m·K
- CTE close to silicon (≈4.5 ppm/°C)
- Excellent for high-power and high-frequency designs
Typical applications:
- IGBT modules
- Power semiconductors
- RF and microwave devices
- EV and charging systems
Limitations: Higher cost and more demanding manufacturing requirements.
Beryllium Oxide (BeO)
BeO offers exceptional thermal conductivity but comes with serious safety considerations.
- Thermal conductivity: ~250 W/m·K
- Excellent electrical insulation
- Toxic when powdered or machined
Typical applications:
- Military and aerospace
- Specialized high-power RF systems
Note: Due to health and environmental regulations, many ceramic PCB suppliers avoid BeO unless explicitly required.
Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
Silicon nitride is gaining popularity in advanced power electronics.
- Thermal conductivity: 70–90 W/m·K
- Extremely high mechanical strength
- Excellent thermal shock resistance
Best for:
- High-reliability power modules
- Automotive and aerospace systems
- Applications with extreme vibration or thermal cycling
Ceramic Circuit Board Material Properties
Understanding material properties is critical when selecting the right ceramic PCB material.
|
Property |
Alumina |
AlN |
BeO |
Si₃N₄ |
|
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
24–30 |
170–230 |
~250 |
70–90 |
|
Dielectric Strength |
High |
Very High |
Very High |
High |
|
CTE (ppm/°C) |
~7 |
~4.5 |
~8 |
~3 |
|
Mechanical Strength |
Good |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Excellent |
|
Cost |
Low |
High |
Very High |
High |
For most commercial designs, alumina or AlN will meet all performance requirements.
Alumina vs AlN vs BeO: How to Choose Between Them?
Choose your ceramic circuit board material based on application requirements:
- Cost-sensitive projects: 96% or 99% Alumina
- High power & heat dissipation: Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
- Extreme thermal performance (limited use): BeO
- High mechanical reliability: Silicon Nitride
A professional ceramic PCB manufacturer can help evaluate trade-offs between performance, manufacturability, and budget.
What Metallization Processes Are Used for Ceramic Circuit Board Material?
Ceramic substrates cannot use standard PCB copper lamination. Instead, specialized metallization methods are applied.
|
Metallization Process |
Characteristics |
Typical Use |
|
DBC (Direct Bonded Copper) |
Thick copper (≥300um) bonded to ceramic |
High-current power modules |
|
DPC (Direct Plated Copper) |
Thin copper (10-30um) with fine-line capability |
RF and signal circuits |
|
AMB (Active Metal Brazing) |
Strong metal-ceramic bond |
High-reliability systems |
The choice of metallization directly affects current capacity, thermal cycling life, and manufacturability. Selecting the wrong process often leads to premature failure.
Considerations When Working With Ceramic PCB Material
When designing or assembling ceramic circuit boards, consider:
- Material brittleness
- CTE matching with components
- Metallization adhesion
- Soldering temperature control
- Panel handling and stress relief
Design-for-manufacturing (DFM) review with experienced ceramic PCB suppliers is highly recommended.
Why Do Ceramic Circuit Boards Fail During Assembly?
Contrary to common belief, most ceramic PCB failures are not material defects. They are process-related issues.
Typical failure causes include:
- Excessive solder reflow temperatures
- Rapid thermal ramp rates
- Poor pad geometry
- Mechanical stress during depaneling
- Inadequate CTE matching
Ceramic substrates are rigid and unforgiving. Assembly processes must be adjusted to respect this behavior. When properly handled, ceramic PCBs exhibit excellent long-term reliability.
How to Design PCBs Correctly for Ceramic Circuit Board Material?
Designing for ceramic substrates requires a different mindset than standard PCB design.
Recommended practices include:
- Avoiding sharp copper corners
- Using rounded pad geometries
- Controlling copper thickness transitions
- Allowing adequate spacing for thermal expansion
- Selecting compliant solder alloys
The goal is not flexibility, but stress management. Proper design dramatically reduces cracking and delamination risk.
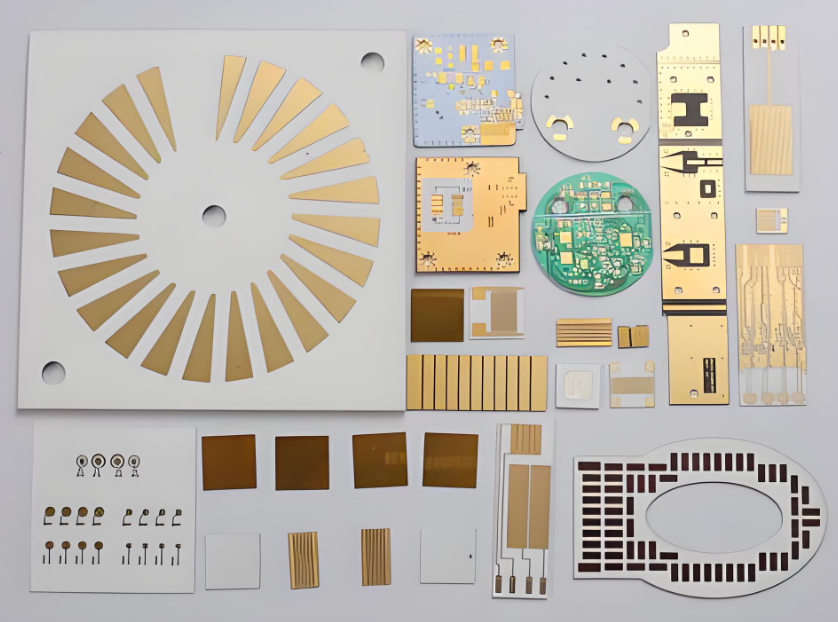
AS9100D Certificated Ceramic PCB Manufacturer – Bstceramic PCB
Bstceramic is an AS9100D-certified ceramic PCB manufacturer, serving aerospace, automotive, and industrial customers worldwide.
Why choose us?
- Strict quality management system
- Full traceability and process control
- Experience with high-reliability ceramic circuit boards
Our Ceramic Circuit Board Material Options
We support multiple ceramic PCB materials, including:
- 96% & 99% Alumina
- Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
- Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
- BeO (on request, compliance required)
Our Ceramic PCB Capability
- DPC / DBC / AMB processes
- Single-layer and multilayer ceramic PCBs
- Thick copper power substrates
- Fine-line high-frequency designs
- Prototype to mass production
FAQs
1. What is the most common ceramic PCB material?
Alumina (Al₂O₃) is the most widely used due to cost and stability.
2. Is ceramic PCB better than FR-4?
For high temperature, high power, and high reliability applications, yes.
3. Can ceramic circuit boards handle high current?
Yes, especially DBC and AMB ceramic PCBs with thick copper.
4. Are ceramic PCBs expensive?
They cost more than FR-4 but offer longer lifespan and better performance.
5. Which ceramic PCB material is best for power electronics?
Aluminum Nitride (AlN) or Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄).
6. Are there safety concerns with BeO?
Yes. BeO is hazardous during machining and requires strict controls.
Ceramic Circuit Board Material Solutions From Bstceramic PCB
EBest Circuit supplies ceramic circuit board material solutions including alumina and aluminum nitride substrates with DBC, DPC, and AMB metallization options.
Our team supports engineers from material selection through final fabrication, ensuring thermal, electrical, and mechanical requirements are met.
If your project requires ceramic circuit board material with reliable performance, contact Bstceramic at sales@bstceramicpcb.com











































 HOME
HOME