High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB: Enabling Reliable Power Electronics and Industrial Systems in Ukraine
Table of Contents
-
Introduction: Why High Heat Dissipation Matters in Ceramic PCBs
-
Ukraine Market Demand for High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB
-
What Is a High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB?
-
Key Ceramic Materials for Superior Thermal Management
-
4.1 Alumina (Al₂O₃)
-
4.2 Aluminum Nitride (AlN)
-
4.3 Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄)
-
-
Thermal Performance Comparison: Ceramic PCB vs FR4 and Metal Core PCB
-
Industrial Applications Driving Demand in Ukraine
-
6.1 Power Electronics & Energy Infrastructure
-
6.2 LED Lighting and Optical Systems
-
6.3 Automotive and Railway Electronics
-
6.4 Military, Aerospace, and Harsh Environment Electronics
-
- Academic Research Supporting High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB
- Design Considerations for High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCBs
- Manufacturing Technologies: DBC, DPC, LTCC, and HTCC
- Why EEAT Matters When Choosing a Ceramic PCB Manufacturer
- Why BST Ceramic PCB Is a Reliable Partner for the Ukrainian Market
- Future Trends: High Thermal Conductivity Ceramic Substrates
- Conclusion & Call to Action
1. Introduction: Why High Heat Dissipation Matters in Ceramic PCBs
As electronic systems become more compact and powerful, thermal management has emerged as one of the most critical design challenges. Excessive heat directly reduces reliability, accelerates material aging, and increases failure rates—especially in power electronics, LED modules, and industrial control systems.
A high heat dissipation ceramic PCB is engineered specifically to address these challenges by combining exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical insulation, and mechanical stability. For industries in Ukraine—ranging from energy infrastructure to transportation and defense—ceramic PCBs are no longer optional but essential.
2. Ukraine Market Demand for High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB
Ukraine’s industrial landscape is characterized by:
- Power grid modernization
- Railway and transportation electronics
- Industrial automation and heavy machinery
- Military and aerospace electronics
These sectors operate under high voltage, high temperature, and long-duty-cycle conditions, where traditional FR4 PCBs fail to deliver sufficient thermal performance.
According to global electronics manufacturing trends, Eastern Europe—including Ukraine—is experiencing rising demand for high reliability PCB solutions, particularly ceramic substrates capable of operating above 200°C with stable thermal dissipation.
3. What Is a High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB?
A high heat dissipation ceramic PCB uses ceramic materials as the base substrate instead of epoxy resin. These ceramic substrates offer:
- Thermal conductivity from 20 W/m·K up to 180 W/m·K
- Excellent dielectric strength
- Low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
- Superior resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion
4. Key Ceramic Materials for Superior Thermal Management
4.1 Alumina (Al₂O₃) Ceramic PCB
- Thermal conductivity: 20–30 W/m·K
- Cost-effective and widely used
- Suitable for industrial control and LED applications
4.2 Aluminum Nitride (AlN) Ceramic PCB
- Thermal conductivity: 140–180 W/m·K
- Ideal for high-power modules and RF applications
- Excellent electrical insulation
4.3 Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) Ceramic PCB
-
Outstanding mechanical strength
-
High fracture toughness
-
Increasingly used in automotive power modules
5. Thermal Performance Comparison: Ceramic PCB vs FR4 and MCPCB
| PCB Type | Thermal Conductivity | Max Operating Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| FR4 PCB | ~0.3 W/m·K | 130–150°C |
| MCPCB | 1–5 W/m·K | 150–200°C |
| Ceramic PCB | 20–180 W/m·K | >300°C |
This data clearly shows why high heat dissipation ceramic PCBs outperform traditional solutions in demanding environments.
6. Industrial Applications Driving Demand in Ukraine
6.1 Power Electronics & Energy Infrastructure
Used in:
- IGBT modules
- Power converters
- Inverters and rectifiers
Ceramic PCBs ensure stable thermal dissipation, extending service life in power stations and renewable energy systems.
6.2 LED Lighting and Optical Systems
High-power LED chips generate intense localized heat. Ceramic PCBs provide:
- Uniform heat spreading
- Improved luminous efficiency
- Extended LED lifespan
6.3 Automotive and Railway Electronics
Ceramic PCBs are increasingly adopted in:
- Traction inverters
- Motor drive units
- Onboard power supplies
Their low CTE minimizes solder joint stress under vibration and thermal cycling.
6.4 Military, Aerospace, and Harsh Environment Electronics
Ukraine’s defense and aerospace sectors require:
- High-temperature resistance
- Shock and vibration stability
- Long-term reliability
Ceramic PCBs meet stringent MIL-grade requirements.
7. Academic Research Supporting High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCB
Peer-reviewed studies consistently confirm the advantages of ceramic substrates:
- Journal of Electronic Materials reports that AlN substrates reduce junction temperature by over 35% compared to FR4 in power modules.
- IEEE publications highlight ceramic PCBs’ role in improving power density and thermal reliability in wide-bandgap semiconductor systems.
- Research from Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing emphasizes the long-term thermal stability of ceramic metallization under cyclic loads.
These studies reinforce the scientific foundation behind ceramic PCB adoption.
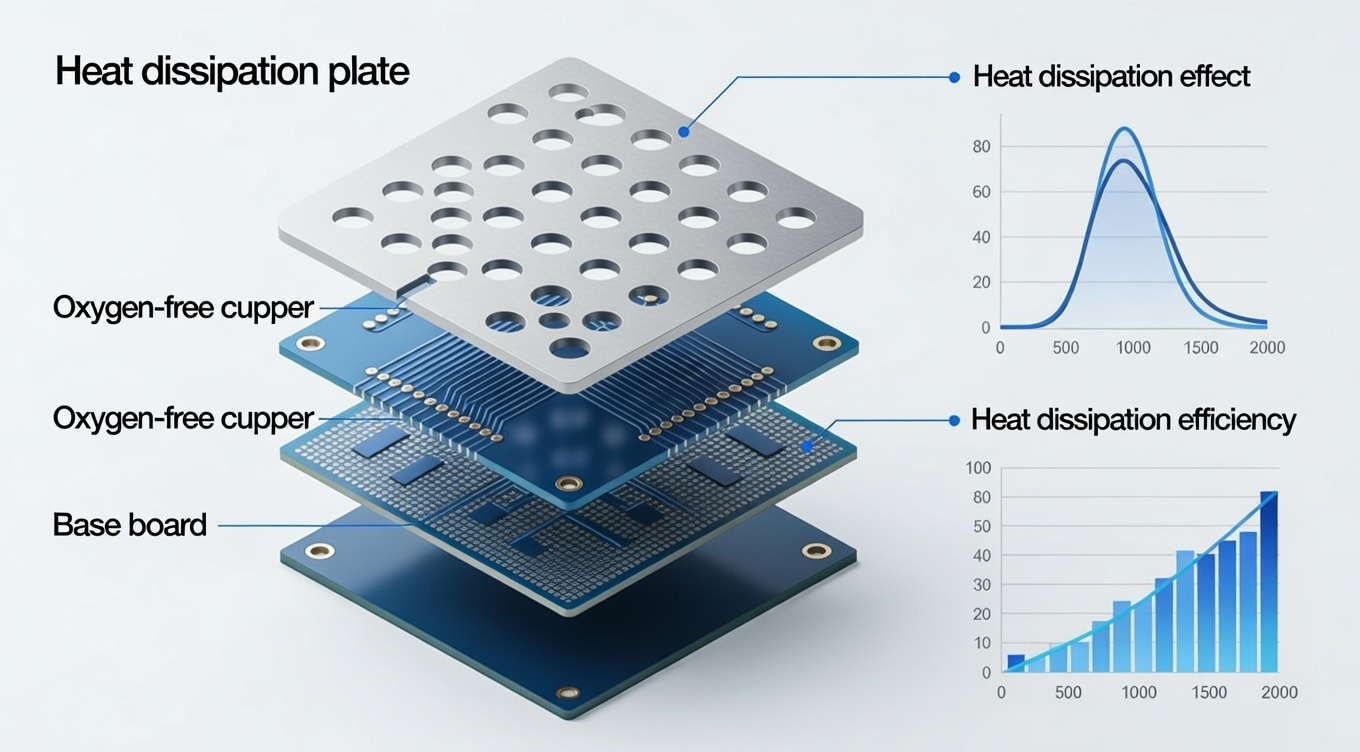
8. Design Considerations for High Heat Dissipation Ceramic PCBs
Key design factors include:
- Copper thickness optimization
- Thermal via placement
- Trace width for current handling
- Metallization method selection
Professional ceramic PCB design support can significantly reduce thermal resistance.
9. Manufacturing Technologies: DBC, DPC, LTCC, and HTCC
- DBC (Direct Bonded Copper): Ideal for power modules
- DPC (Direct Plated Copper): Fine-line capability for high-density circuits
- LTCC PCB: Multilayer integration for RF and sensor modules
- HTCC PCB: High-temperature co-fired ceramic for extreme environments
10. Why EEAT Matters When Choosing a Ceramic PCB Manufacturer
Google EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) aligns closely with real-world supplier evaluation:
- Proven manufacturing experience
- Transparent material data
- Engineering documentation
- Consistent quality control
BST Ceramic PCB emphasizes technical transparency and application-driven solutions.
11. Why BST Ceramic PCB Is a Reliable Partner for the Ukrainian Market
BST Ceramic PCB offers:
- In-house ceramic substrate processing
- Al₂O₃, AlN, and advanced ceramic options
- Custom prototyping and volume production
- Engineering support for thermal simulation
12. Future Trends: High Thermal Conductivity Ceramic Substrates
According to Google Trends and industry forecasts:
-
Demand for AlN and Si₃N₄ ceramic PCBs is accelerating
-
Wide-bandgap semiconductors (SiC, GaN) require superior thermal substrates
-
Ceramic PCBs are becoming standard in high-power electronics
13. Conclusion & Call to Action
A high heat dissipation ceramic PCB is no longer a niche solution—it is a strategic requirement for industries operating under thermal stress. For Ukraine’s power, transportation, and defense sectors, ceramic PCBs offer unmatched reliability and performance.
BST Ceramic PCB is committed to delivering advanced ceramic PCB solutions tailored to demanding applications.











































 HOME
HOME